Simple Guide to SOP Management in Pharma Industry
The complexity of manufacturing, especially in the pharmaceutical industry, is multifaceted and significantly high. The direct impact of pharmaceutical products on consumer wellness and health necessitates an unwavering commitment to getting it right every time.
Standard Operating Procedures (SOPs) Management, a fundamental framework that not only delineates the standardized steps and processes but also stands as a mandatory compliance requirement in the industry.
SOPs serve as a vital blueprint, offering clarity and guidance for both seasoned professionals and newcomers within an organization. For newcomers, in particular, SOPs act as a foundational resource, facilitating their assimilation into the organizational culture, functions, and processes with utmost clarity, leaving no room for confusion.
Looking to streamline SOPs in pharma? “Request a Demo” today.
The upcoming blog aims to delve deep into the world of SOPs in pharmaceutical industry, providing comprehensive insights into their significance, implementation, and impact.
Stay tuned to uncover a detailed understanding of SOPs and their pivotal role in ensuring quality, compliance, and efficiency within pharmaceutical manufacturing.
Table of Content:
- What is SOPs in Pharma Industry?
- Why Pharmaceutical SOPs are Important?
- Benefits of SOP in Pharmaceutical Industry
- Factors Important for Establishing Guidelines for SOPs in Pharma
- How to Manage Pharmaceutical SOPs?
- Final Points
What is SOPs in Pharma Industry?
SOPs (Standard Operating Procedures) is crucial in the pharmaceutical industry to ensure tasks are carried out consistently, accurately, and in compliance with regulations.
Here’s an example list of protocols for entering a laboratory in a pharmaceutical organization:
- Personal Protective Equipment (PPE): Before entering the lab, ensure you’re wearing the designated PPE, such as lab coats, safety goggles, gloves, and closed-toe shoes.
- Hand Hygiene: Wash hands thoroughly with soap and water or use provided hand sanitizers to maintain cleanliness.
- Authorization and Access: Only authorized personnel with proper credentials and training are allowed entry. Access control measures must be adhered to strictly.
- Equipment Check: Before commencing work, ensure that all necessary equipment is in working condition and calibrated if required.
- Documentation Review: Review and understand the specific SOPs related to the tasks to be performed in the lab.
- Waste Disposal Procedures: Familiarize yourself with the proper disposal methods for various materials, including hazardous waste, sharps, and general waste.
- Chemical Handling: Follow established procedures for handling, storage, and disposal of chemicals, including appropriate labeling and Material Safety Data Sheets (MSDS).
- Emergency Procedures: Understand emergency protocols, including the location of emergency exits, eyewash stations, fire extinguishers, and emergency contact information.
- Cleanliness and Organization: Maintain cleanliness and organization within the lab space, ensuring all work areas are tidy after use.
- Sampling and Contamination Prevention: Adhere to specific procedures for sample collection, avoiding cross-contamination, and maintaining a sterile environment when necessary.
- Equipment Log: Maintain a log for any equipment used or experiments conducted, noting details for reference and traceability.
- Report Any Anomalies: Immediately report any accidents, spills, equipment malfunctions, or deviations from procedures to the designated authority.
These rules show the careful and organized steps needed before going into a pharmaceutical lab. Each step is really important to make sure everything is safe, follows the rules, and keeps the experiments or work in the lab reliable.
The example is not an ideal one, but it can give you a fair idea of what it actually is. Likewise, for every process, there are set rules, documented, approved, and verified which are known as SOP.
QualityPro, an eQMS (Electronic Quality Management System) Software provides a comprehensive solution for organizations to centralize and manage all SOPs in a single, accessible location. Its Advanced SOP in pharma functionality allows for the maintenance and management of Master SOPs and associated records efficiently.
Why Pharmaceutical SOPs are Important?
As stated earlier, SOPs lay down a blueprint for necessary actions to be taken while performing a task or following a process. Let us discuss why SOPs are so important for a pharmaceutical industry:
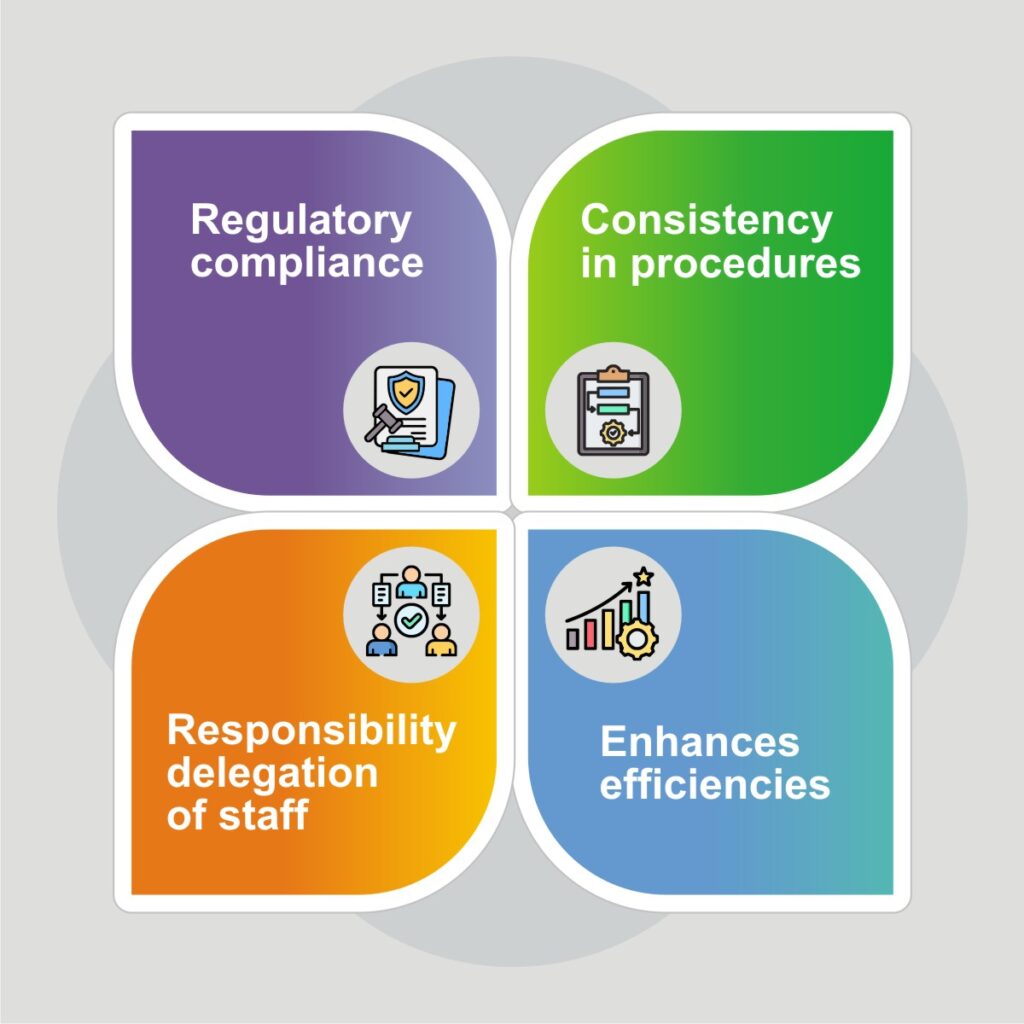
- Regulatory Compliance: Compliance with regulatory standards is essential in the pharmaceutical sector. Documented SOPs ensure that processes align with regulatory requirements. Regulatory organizations inspect SOPs to verify adherence, and any deviation or absence of SOPs could lead to severe penalties or regulatory actions.
- Consistency in Procedures: Maintaining consistency in manufacturing processes is critical. SOPs ensure that each drug batch is produced with the same procedures, facilitating consistent results and effects on patients. This consistency is fundamental for ensuring the safety and efficacy of pharmaceutical products.
- Enhanced Efficiencies: SOPs are dynamic documents that evolve with industry advancements. Continuous improvements and updates to SOPs enhance the efficiency of processes. These improvements contribute to better quality products and streamlined operations.
- Responsibility Delegation: SOPs clearly outline roles and responsibilities for various procedures. This delineation reduces overlap and ambiguity, ensuring that everyone understands their job roles and responsibilities, promoting accountability and awareness among staff members at all levels within the organization.
Absolutely, defining job responsibilities within SOPs not only streamlines processes but also contributes to cost savings and maximizes individual potential within an organization.
Benefits of SOP in Pharmaceutical Industry
- Performance Evaluation and Planning: SOPs provide a benchmark for assessing personnel performance. Managers can easily evaluate adherence to SOPs, ensuring standards are met. Employees, armed with SOPs, can plan their work schedules more effectively, knowing the standards they’re expected to achieve.
- Scalability and Consistency: As organizations grow or expand across multiple facilities, maintaining consistent output becomes critical. SOPs ensure uniformity across all sites by standardizing procedures, enabling each facility to produce the same quality results, crucial for maintaining consistency in pharmaceutical products.
- Knowledge Continuity and Transfer: SOPs act as a repository of knowledge. In instances where key personnel depart, the documented SOPs become invaluable resources, ensuring that critical knowledge and procedures are preserved. This helps prevent disruptions and ensures that operations continue at the same standard even in the absence of key individuals.
- Effective Training Tool: SOPs serve as comprehensive guides for newcomers. Instead of relying on scattered or incomplete information from colleagues, new recruits can refer to SOPs for precise and detailed procedures. This minimizes confusion, errors, and ensures that newcomers receive accurate and consistent information during their training.
In essence, SOPs not only standardize processes but also serve as crucial tools for performance evaluation, scalability, knowledge transfer, and effective training within the pharmaceutical industry. Their multifaceted role significantly contributes to operational efficiency and consistency.
Factors Important for Establishing Guidelines for SOPs in Pharma
Developing comprehensive guidelines for SOP is quite crucial to ensure consistency in product and regulatory compliance.
Consider the following factors while formulating the SOPs of your pharmaceutical organization:
- Uniformity and Standardization: Consistency in format, structure, language, and style across all SOP documents ensures clarity and promotes effective communication within the organization. This uniformity facilitates ease of understanding for all stakeholders.
- Legal and Regulatory Compliance: Adherence to legal and regulatory requirements is non-negotiable. SOPs should incorporate specific measures and guidelines to ensure compliance with these obligations, maintaining the highest standards of quality control.
- Clarity and Simplicity: Avoid complex technical language in SOPs. Using straightforward, action-oriented language in an active voice makes procedures easier to understand and follow, benefiting all personnel involved.
- Comprehensive Content: SOPs should leave no room for guesswork. They should contain exhaustive information, detailing procedures, timelines, and quality standards precisely. Including even the minutest information ensures thoroughness and clarity.
- Stakeholders’ Involvement: Involving key stakeholders, such as department heads, process heads, and IT heads, in the SOP development process is essential. Their input ensures practicality and relevance in the guidelines, aligning them with actual operational needs and challenges.
By considering these factors, a pharmaceutical organization can develop SOPs that are not just compliant but also comprehensive, clear, and practical for effective implementation across the organization. These SOPs serve as critical documents guiding personnel in adhering to standardized processes and maintaining the highest quality standards.
How to Manage Pharmaceutical SOPs?
SOPs once drafted, verified, and approved must be stored and kept secure in a quality management software for pharma industry like QualityPro.
Pharma SOP software offers a host of management capabilities to effectively access, manage, edit, and secure all the SOPs of the pharmaceutical organization.
QualityPro offers a robust set of capabilities for effective management of SOPs within a pharmaceutical manufacturing industry:
- Advanced SOP Functionality: This feature allows the maintenance of master SOPs and their corresponding records. It provides a structured system for sorting, accessing, and categorizing SOPs, ensuring organized and efficient management.
- Access Control: QMS system ensures controlled access to SOPs, permitting entry only to authorized personnel. This access control adds an additional layer of security against data breaches. Moreover, it allows for specific controls over viewing, editing, or other actions based on job roles, enhancing data security.
- Stamping for Tracking: The QMS solution offers user and date stamping, creating a comprehensive trail of who accessed or utilized the SOP and when. This tracking capability ensures accountability and traceability within the system.
- Guideline Attachment: QualityPro allows the attachment of supplementary documents, guidelines, or rules to SOPs. This feature enhances clarity and management of SOPs by providing additional context or explanatory materials, ensuring comprehensive understanding and effective implementation of procedures.
These functionalities collectively contribute to a robust and secure system for managing SOPs, ensuring compliance, security, and traceability within the pharmaceutical industry.
Final Points –
SOPs in pharmaceutical industry play a critical role as the backbone of pharma manufacturing, dictating standardized procedures and ensuring consistent, reliable results. Mismanagement, uncertainty, or scattering of SOPs can lead to chaos and deviations in outcomes, which is particularly impactful and risky in the pharmaceutical industry.
In this context, effective management of SOPs becomes paramount for pharmaceutical manufacturers. QualityPro takes on this challenge robustly by offering comprehensive solutions to manage, track, store, secure, revise, and distribute SOPs in the most effective and efficient manner.
For pharmaceutical manufacturers grappling with SOP management challenges, QualityPro provides a reliable solution. By clicking here, organizations can streamline their SOP processes, ensuring adherence to standards, regulatory compliance, and the maintenance of top-notch quality in pharmaceutical operations.
QualityPro’s tailored capabilities aim to alleviate the complexities associated with SOP management, enabling pharmaceutical organizations to uphold the highest standards and achieve operational excellence without compromising on regulatory compliance or product quality.