Essential Elements of Quality Management in Food Industry

The globalisation has made the manufacturing market more competitive, by offering new opportunities to businesses old and new. This should not be considered as a threat to the survival of existing manufacturers; in fact, it is a challenge that they should take up. Because this challenge, actually poses an opportunity to gain customer loyalty through the enhanced products and improved services offered in the quest to stand up to the challenge.
By enhanced products we mean ones—that suitably cater to the specific needs and concerns of the customers. Also, when it comes to competitiveness, one obvious question that arises is- “With the rising competition bar, what makes the top manufacturers stand out from the league?”
The answer to this question is “quality of their own products & services”. By maximising suitability and quality of their products for the consumer usage, manufacturers succeed in excelling in their field— and thus in building a sustainable brand image.
Looking for a digital solution? Explore our “QMS software for food industries“
Therefore, to become a successful manufacturer, robust quality control, is of utmost importance. For which, manufacturers need to opt a feature-rich quality management system. But if you are a tenderfoot, then before implementing a quality software, knowing the concept of quality and food quality management is essential.
This blog takes you to a knowledge-intended journey of exploring the term “quality” and the essential elements of a QMS.
The Quality Concept-
“Quality is a comprehensive term that includes two meanings: product characteristics that lead to customer satisfaction and the absence of failures. Still, this does not defines “Quality” as a whole.
The customer needs are not only related to these two intrinsic characteristics of the product, but also to its availability in the market, it’s appropriate pricing and suitable packaging.
These specifications altogether ensure that the customer will buy a safe product standing at par with what is mentioned on the label, without having any health threats.
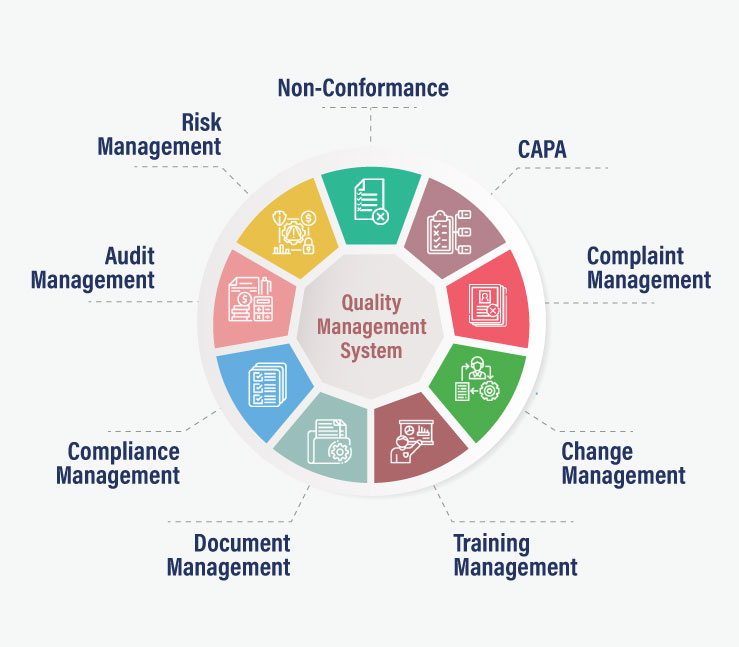
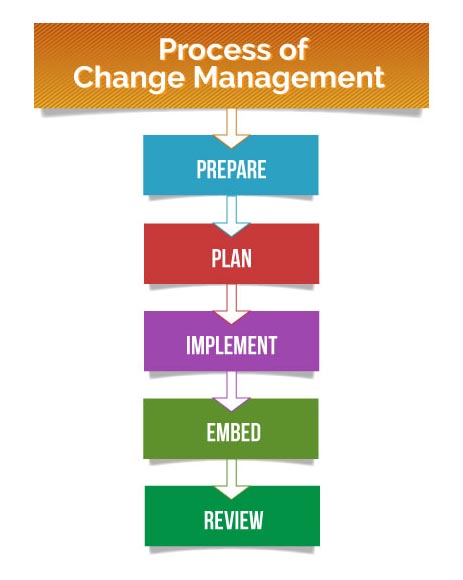
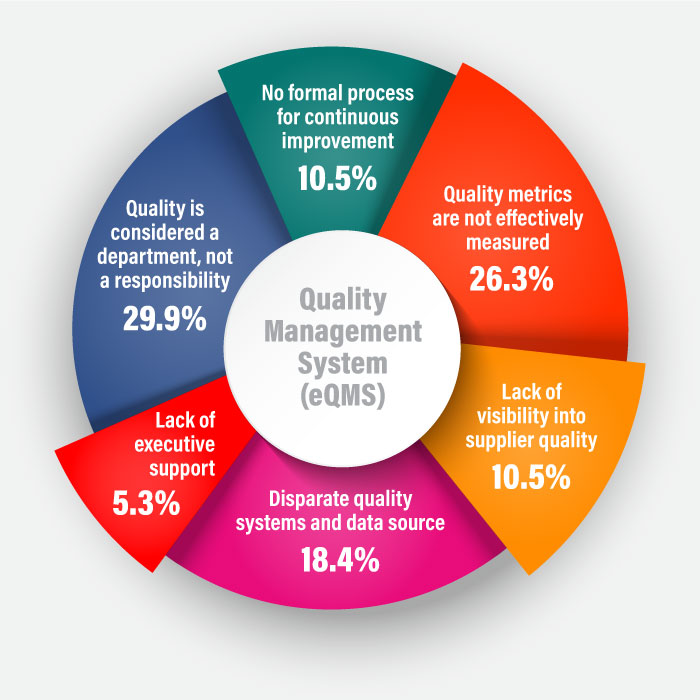
For these objectives to be achieved, it is necessary to have an efficient food quality management system in place that ensures operational excellence at each level of the organisation. Talking of an ideal QMS, it must have the following capabilities.
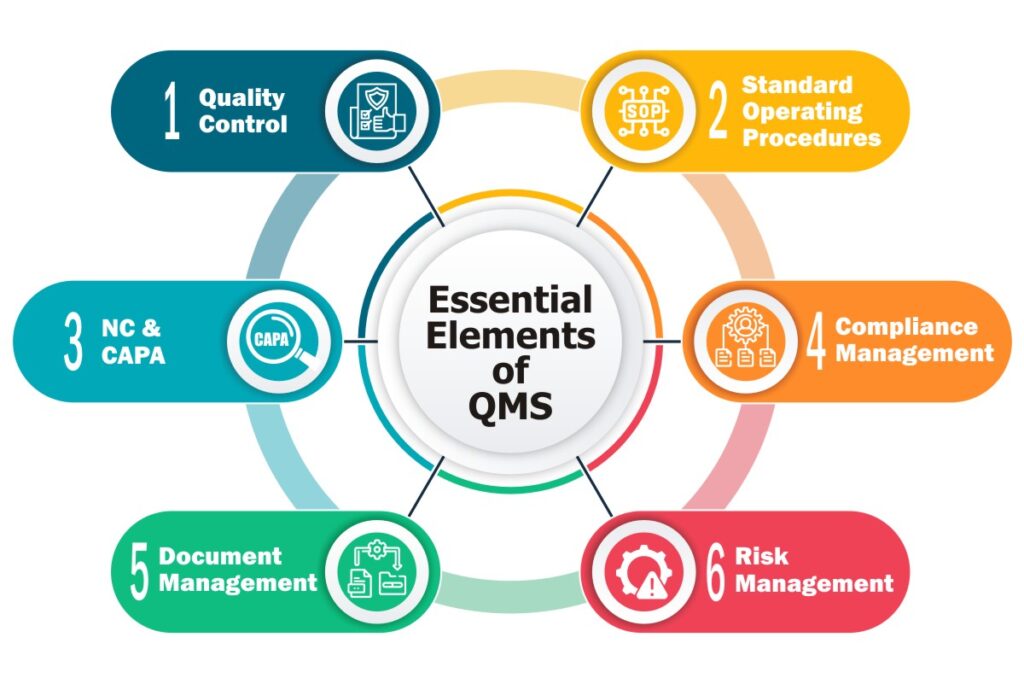
Quality Control- To ensure safety and quality of the food for consumers, adhering to quality requirements becomes a mandate for the food manufacturers. With the absence of quality control procedures, the contaminated foods can easily make way to the markets.
In avoiding such situations, the Quality Control module of a Quality Software plays a key role. Because it allows manufacturers to create and apply quality tests on the products, at all important junctures of the food supply chain-, that too with set target values.
This ensures quality throughout the product lifecycle: i.e., when materials enter the facility, when they are put ahead for production, and when they are being shipped to the customers. Also, based on the test results of pass/fail, manufacturers get the convenience of accepting and rejecting products accordingly.
Standard Operating Procedures (SOPs) – Food manufacturing refers to the process of turning fresh ingredients into consumable food products. This includes the process of high-volume mixing of multiple ingredients that too in a set order, to manufacture finished goods. These finished goods must have uniform consistency. Even a small deviation in the procedure, could lead to fluctuations in the product quality of the finished goods.
Therefore, documenting processes in the form of Standard Operating Procedures (SOPs) helps organisations ensure error-free and consistent processes throughout the supply chain. This is the reason why the Advanced SOP Module turns out to be one of the prominent features that should not be given away with.
Compliance Management- Throughout the supply chain, adherence to set safety laws imposed by the regulatory bodies ensures that the food item is not unsafe, misbranded, or low-graded for the human consumption.
This feature helps manufacturers comply with major regulatory standards, including GFSI, ISO, HACCP, GMP, and FDA requirements.
See how QMS simplifies food compliance— “Request a Demo“
Non-Conformance (NC) & Corrective Action Preventive Action (CAPA)- Non-conformance reports that there is something wrong with the process or product due to which the outcome fails to match the required product specifications. In situations like this, the NC/CAPA functionality of an efficient QMS comes to the rescue. It helps in successfully dealing with every type of non-conformity that could occur such as:
- Product non-conformity– Which relates to product issues identified during quality management or by customer complaints.
- Process non-conformity– Which relates to downtime, machine problems, operational inconsistency, etc.
- System non-conformity– Which is identified by internal audit system
- Material non-conformity– Which occurs due to expired materials, ingredients
The NC functionality finds the root cause of the occurred non-conformity, wile the CAPA suggests the required corrective needed to be applied, and prevents its recurrence, comes out as an un-negotiable part of the QMS system.
Document Management- This capability is essential to control the pile of documents a food business needs to manage for several reasons. This includes formula/recipe details, SOPs, compliance policies, training manuals, recall procedures, labels, etc. These crucial records must be accessible when required, and hence needs to be systematically managed.
But manual management of these documents could lead to maximised manpower requirement & minimised productivity. That’s the reason the document management feature can’t be ignored in the list of essential elements of a Quality Management system. It automates the task of creating, storing, managing, and retrieving the documents when required— and becomes a significant contributor in enhancing the organisational productivity.
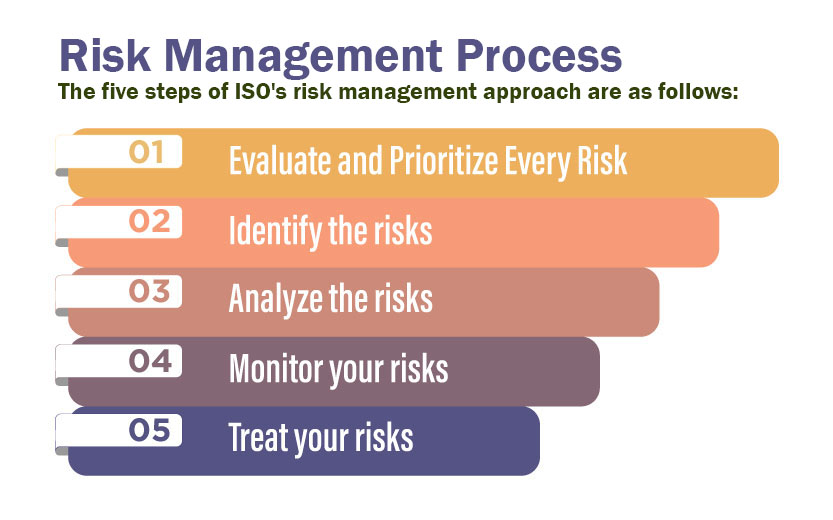
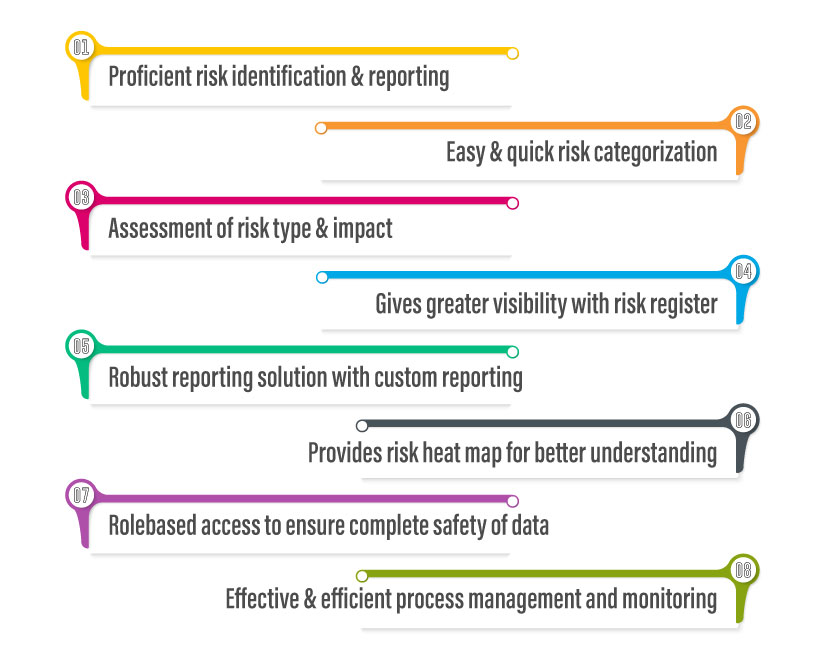
Risk Management- It is the act of setting up prevention strategies to avert potential issues from occurring. Actually, the risk management feature efficiently identifies the potential areas that are vulnerable to business helping organisations carry out necessary actions in response. Though there could be numerous areas of risks in a food manufacturing business, but, the prominent ones out of all are:
- Supply chain risks– Threats from the quality of materials arriving at the facility
- Cyber risks– Data corruption, data loss, data manipulation
- Natural Hazards– Equipment failure, earthquake, Fire outbreak, etc.
A risk management system can help you manage, track and mitigate these risks and that’s the reason why a proper risk management approach is a must-have feature for a robust food quality management system and should not be overlooked by the manufacturers.
Final Thoughts-
Food manufacturing involves processing of highly sensitive and perishable items, which makes it more challenging for the manufacturers of that industry to sustain. Hence, right from the purchasing of raw materials to delivery of finished goods, everything needs to be not just streamlined and organised, but inspected too.
For this, other than a good QMS software like QualityPro, no other strategy would deliver better results. If you are also looking to inject a culture of quality into your business, then get in touch with our team of experts today.
Looking to improve quality practices in food and beverages? “Contact Us“